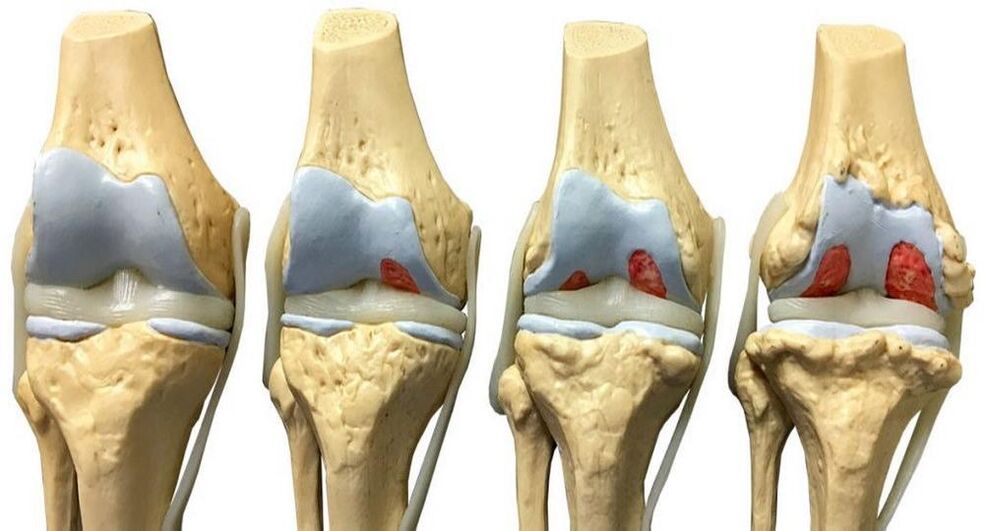
Arthropathy of the knee joint is understood as a decrease in the performance of cartilage due to its bending and destruction. Other terms are used to refer to this disorder -ArthropathyandDeformed osteoarthritis. Currently, several treatments for the disease are used: specific options are selected based on the individual characteristics of the patient.
disease specificity
Knee osteoarthritis usually develops in a progressive manner. Typically, it occurs in women and older adults who are overweight or have venous defects. The disease can occur on one or both knees at the same time.
The main stages of development of knee joint disease:
- initial. The depreciation parameters of the joints are reduced due to the mutual friction and roughness of the cartilage. Crack formation is sometimes observed.
- second. During this stage, the bone begins to be covered with growths (osteophytes). On the inner surface of the joint pocket, the curvature is fixed, and stiffness is observed during work of the limb. As a result, the knee joint gradually reduces its function. A decrease in the distance between the tibia and femur was observed due to a reduction in the thickness of the interchondral lining.
- third. If nothing is done, pain in the knee area can become permanent due to irreversible damage to the cartilage tissue. Patients at this stage are no longer able to move normally.
The first symptoms of knee arthropathy are good reasons to consult a specialist. Otherwise, there is a real danger of becoming disabled.
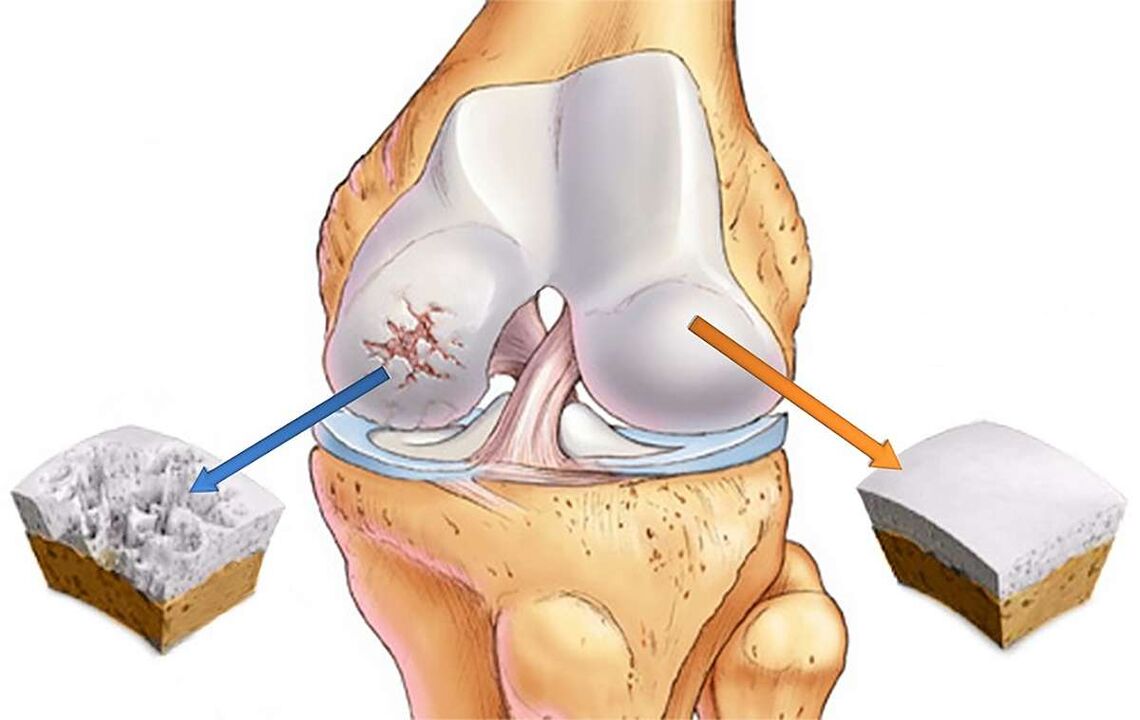
Why does joint disease occur
The main reasons for the development of knee joint disease:
- genetic predisposition;
- Temporary immobility of the knee joint due to injury;
- surgical removal of the meniscus;
- High physical activity, sustained hypothermia;
- Obesity, overweight problems;
- ligament rupture (weakening);
- other joint disorders (arthritis, swelling, various inflammations);
- Failure of normal metabolism, calcium deficiency in the body;
- Flat feet (a low center of gravity can increase stress on the joints);
- Stress, general fatigue, lack of sleep.
symptom
Possible signs of knee osteoarthritis:
- Knee pain. On the background of physical exertion, the pain appears suddenly. In the first stage, we are talking about low back pain that is barely noticeable, and later the disease becomes more severe.
- Visual violation of the shape of the knee. It happens later.
- Effusion, Baker's cyst. These are tangible seals in the back area of the knee joint.
- The appearance of cartilage tightening occurs on the background of severe pain. This indicates a second or third stage of arthropathy.
- Inflammation of the area inside the joint pocket. It manifests as edema and increased cartilage.
- Stiffness of the knee joint due to severe pain until it is completely immobilized. This occurs late in the disease.
treat
Knee arthropathy can only be effectively treated with a comprehensive approach. Modern medicine is not yet able to provide a specific drug that will eliminate the disease. The success of the treatment program depends on the timely detection of the problem, which allows you to start fighting knee disease at an early stage.
To begin treatment, specialists pursue several goals:
- reduce pain symptoms as much as possible;
- restores normal nutrient flow to the joints;
- increase the strength of blood circulation in the knee area;
- Restoring the function of the supporting muscles in the problem area;
- move the knee as far as possible;
- Expand the space between the connected bones.
The exact treatment algorithm is determined on an individual basis. Distinguish between conservative and surgical techniques.
conservative law
This method is used in the early stages of disease onset and is the use of various drugs and therapeutic exercises.
Painkillers, Anti-Inflammatories
To eliminate or reduce knee pain, doctors often prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In pharmacies, they are represented by tablets, ointments and injections. Warming and anesthetic gels, ointments, and patches have shown good results in pain relief.
In this case, a positive result is usually obtained within 3-4 days. It should be understood that these drugs do not eliminate the disease, but only relieve pain. It is recommended to take pain relievers only on the advice of a specialist and only to resolve intolerable pain. The truth is that NSAIDs can cause a variety of side effects (especially the gastrointestinal tract).
hormone drugs
In some cases, a doctor may prescribe hormone injections to relieve knee osteoarthritis pain. This approach is used when the effectiveness of NSAIDs is weak in the context of disease progression.
Short-term (1-10 days) use of corticosteroids during periods of worsening arthropathy and knee effusion.
chondroprotective agent
Restoring and nourishing the cartilage layer, the so-called, at the beginning of the development of the disease. Chondroprotective agents (glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate). Glucosamine initiates the cartilage regeneration process, corrects metabolism and stops destructive processes. Chondroitin sulfate disarms dangerous enzymes and increases collagen (the protein that nourishes cartilage with water). According to leading physicians, these drugs are currently showing the greatest positive effect in the treatment of arthropathy.
In particularly critical situations, when cartilage tissue is severely abnormal, chondroprotective agents are ineffective. When prescribing glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate, doctors specify specific daily doses. Positive results are only possible when these drugs are taken systematically. When sold, they are represented by tablets, capsules, injections, gels.
vasodilator
To eliminate spasms in the vascular system and optimize blood flow and metabolism in the knee area, doctors prescribe funds for vasodilation. Often, they are used in combination with chondroprotective agents. If the fluid in the knee does not collect on the background of arthropathy, it is possible to rub the joint with warm ointment and participate in a therapeutic massage.
Hyaluronic acid
In its chemical composition, this substance is very close to the intra-articular fluid. When the acid is introduced into the joint, it creates a film that protects the cartilage from rubbing against each other. This medicine can be used when the condition worsens.
therapeutic exercise
For knee osteoarthritis,Resort to exercise therapy, but only under the strict supervision of an attending physician or an experienced coach. Self-medication is strictly prohibited, as any careless movements and loads carry great risks. Correct use of physical therapy exercises can help keep your joints working, eliminate muscle spasms, and relieve symptoms of discomfort. Physiotherapy exercises are strictly prohibited when the condition is aggravated or inappropriate.
physiotherapy
Correctly applied, physical therapy techniques can significantly reduce knee pain, reduce inflammation, and improve the flow of nutrients to joint tissues. Before prescribing physical therapy, an orthopaedic surgeon performs a detailed diagnosis of the problem area, prescribes general and special tests, and sends ultrasounds or X-rays. This approach allows you to draw an actual picture of the problem and choose the best approach.
The following types of physical therapy have good analgesic effects:
- UV exposure. Due to exposure to UV light, nerve endings are less sensitive and pain is lessened. Usually, it is prescribed at a later stage of the disease. The standard duration of treatment is 7-8 courses.
- Local magnetic therapy. Improves patient's overall health by reducing pain, inflammation, muscle spasms. Magnetic therapy is usually prescribed when symptoms of knee arthropathy are first fixed. The standard number of procedures is 20-25 times of 30 minutes each.
- Infrared laser therapy, UHF, SMW devices, ultrasound, therapeutic baths, etc.
If the disease has entered the stage of malnutrition and deformity, doctors recommend hygienic treatment. Compile a list of specific procedures after careful study of the patient's medical history.

Operation
This method, with proper implementation, can partially or fully restore the work of the knee joint. The surgical intervention algorithm was developed taking into account the degree of cartilage tissue destruction, the degree of inflammation, the amount of fluid collected, etc. Typically, surgical intervention is performed in the advanced stages of arthropathy. This approach means partially or completely replacing the affected joint with an endoprosthesis.
The main methods of surgical treatment:
- Arthrodesis. During the procedure, the surgeon positions the leg in the most comfortable position for the patient and then immobilizes the knee joint. Defective cartilage is completely eliminated. This aggressive approach only works in extreme cases.
- Arthroscopic debridement. It is used in the second stage of knee joint development. Surgical removal of damaged cartilage tissue, which allows you to save the person pain for several years (usually 2-3 years).
- Built-in prosthesis. In this case, the knee joint or its independent part is replaced with a plastic, ceramic or metal implant that completely replicates the natural joint anatomy. Today's endoprosthesis is considered the most effective way to restore a mature lifestyle to a knee with arthropathy in the next 15-20 years.
Effective planning and implementation of surgical treatment can improve the patient's health and restore mobility (partial or complete). At the same time, it is necessary to understand that a longer recovery period is required after surgery, including physical therapy exercises, physical therapy, and dieting.
recovery
On average, the recovery period after surgery takes 90 days:
The main tasks of rehabilitation:
- restore the patient's ability to perform normal activities;
- Optimize the function of muscles and joints;
- Create a protective block for the prosthesis.
After 2-3 days of drainage, you can try to walk carefully. To relieve pain, doctors prescribe medicines that have a cooling effect. Mild pain symptoms after surgery sometimes persist for up to a year: this is because the prosthesis takes time to heal. Older patients took longer to recover: To relieve their condition, they took NSAIDs. In some cases, the attending physician will prescribe hormonal preparations that have dramatic effects.
A week later, the patient entered a rehabilitation center under the care of an experienced physical therapist. The individual characteristics of the body are taken into account when developing an exercise therapy program. Classes are held regularly (every day) with a gradual increase in load: this prevents injury and tissue rupture.
post-discharge period
At the end of his stay in the rehabilitation center, the patient is discharged and he is given detailed advice on his future lifestyle. Dance and light gymnastics are allowed 6 months from the date of surgery. As for heavy loads (speed runs, jumps, sports competitions, heavy squats), they must be completely ruled out. Otherwise, the prosthesis will fail quickly.
Do not lift heavy objects over 25 kg. Inside the dwelling, it is necessary to install supporting handrails: they are placed on the stairs, in the shower and in the bathroom. All furniture must be functional (especially chairs). These and other measures will maximize the lifespan of the prosthesis. You should also be prepared for postoperative arthropathy of the knee, which can last up to 3 years.
prevent disease
The best way to deal with any disease is to prevent it from happening.
Effective WaysPrevent knee osteoarthritis:
- Proper nutrition to maintain a normal weight. It is best to remove fat and fried foods, alcohol, coffee, etc. from your diet, and an experienced nutritionist can provide detailed advice.
- Be careful when exercising. It is desirable to reduce the load on the joint as much as possible.
- Be aware of any disease (especially infectious disease), treat it properly, and avoid the chronic phase.
- Pay attention to your posture and don't ignore diseases of the bones and spine.
- Incorporate gentle physical activity (biking, swimming, walking, joint-strengthening exercises) into your routine.
- Avoid any self-treatment options for knee arthritis. At the first symptoms of the disease, you should contact the clinic immediately.
- Live a peaceful lifestyle without stress and lack of sleep.
- Take steps to strengthen immunity (hardening, taking vitamins).
- Wear warm clothes in cold seasons.
By applying the principles of a healthy lifestyle to your life and seeking prompt medical help, you can minimize your risk of developing knee arthropathy. When choosing a clinic, priority should be given to established treatment centers with modern equipment.